The brain guides the eye to look from one place to another. Peripheral vision assists in this process. It attracts the foveal (central) vision, “where to look”. Peripheral vision can’t get detailed information like color, size and shape, but it has strength like movement, contrast and sound. A designer can engage user by using these strengths of peripheral vision.
What is foveal and peripheral vision?
What we see directly in front of our eyes is called foveal (central) vision. What we see off the side is our peripheral vision. A normal visual field of human is around 170 degree, with 100 degrees comprising the peripheral vision.
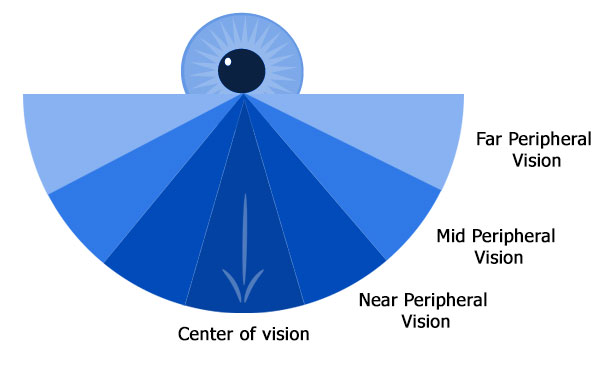
Foveal vision is located in the center of the retina. It has photoreceptors called “cones” that can perceive even small details of any element. We can perceive small details when we focus on any object.
There are photoreceptors called “rods” in the periphery of retina. They are low in resolution and low color sensitive. But, they attract the foveal vision to look into. Peripheral vision allows us to see all object around us without moving head or eyes.
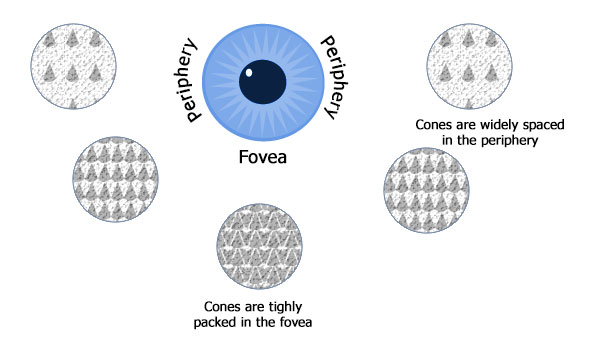
Eyes work in harmony with brain to create the image that a human can perceive
Retina in our eyes sends the signal to brain and retina has 2 types of photoreceptors rods and cones.
| Cones | Rods |
|---|---|
| Foveal Vision | Peripheral Vision |
| Direct | Indirect |
| 6 millions in number | 120 millions in number |
| High color sensitivity | Low color sensitivity |
| Location is central of retina | Location is on the edge or periphery of retina. |
| High Resolution | Low Resolution |
| Work better in bright light | Work better in the dim light |
The central part of an image falls on the foveal vision. It is processed with higher resolution than the part in peripheral vision.
Importance of peripheral vision in everyday life
- Sports people use peripheral vision constantly to see the placement of players around.
- A chess player focus on specific square but see the entire board from peripheral vision.
- We sense the danger quickly from our peripheral vision like a car approaching while crossing.
- Peripheral vision helps to see in night.
Why peripheral vision is important in the UX design?
Peripheral vision has low sharpness. However, it quickly detects motion and sound. It gives cues to foveal (central) vision to move an eye toward what is important on a web page. In simple terms it guides the foveal vision to look into desired area in the user interface.
The eyes look, but the brain sees
Users are not capable of seeing the whole site at once, they scan it with the guidance of peripheral vision. Their eyes jump very fast to scan the page. You can intentionally redirect users from one area to another. Proper visual hierarchy and content grouping help users scan the web page.
Colors for peripheral vision
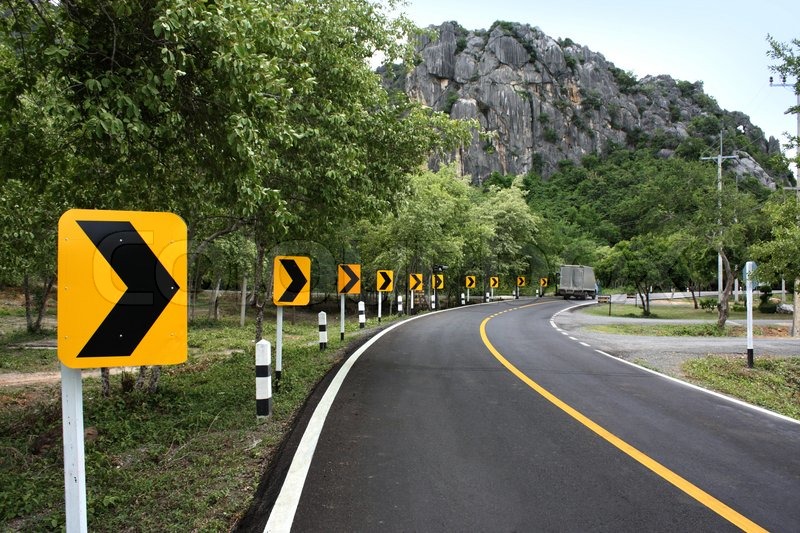
Color vision is sensitive to foveal (central) vision and declines steeply in the periphery. But peripheral vision attracts towards high contrast colors especially yellow color. Our vision is most sensitive to yellow color. This is why yellow is used for road signs, traffic lights, and school buses. It can draw attention and is hard to miss, even from a distance or in bad weather.
Yellow color should be used for any important message where user’s immediate attention is required.

Selective disregard and intentionally getting the focus
Users ignore the elements that enter in periphery vision and look like irrelevant, unimportant or familiar to them. But subconsciously eye is shifted to something important unfamiliar entry in the peripheral vision. User gets the attention by altering size, color, image, font or adding animation.
Messages and notification should be within our peripheral vision. For example, when a user clicks a button, the action’s response should be near the button. Alternatively, add some motion for peripheral vision. Otherwise, an important message in the peripheral vision can be ignored by the user.
Message in red color can also be missed when other elements around it are red
Visual attention from peripheral to foveal
Visual information coming from periphery guides the foveal vision; it plays its role even in filled and stuffy UI. It simplifies the task of user with the help of preattentive attentional cues. A classic example is counting the number of 3s in a random set of numbers. This demonstrates visual attention from peripheral to foveal vision.

You must scan all numbers to count 3s in the above image. But if we change the hue, all 3s become easier to see.

Motion for peripheral vision
Peripheral vision is most sensitive for motion. Periphery of the eye has more rods than cone cell which process motion (even in dark) faster than cone cells. It reacts to motion very fast. Motion is a very powerful tool to grab attention or direct the user to the desired area of the page. But it needs to be used very carefully as excessive use of animation can lead to distraction.
Peripheral vision can detect only one type of motion at a time
Some facts about animal’s peripheral vision
- Dogs can see seven times better at night than humans. They have a higher number of rod cells in their central vision. Dogs have very few color sensitive cones in their eyes – almost monochromatics.
- Sharks sees black & white, they don’t see colors but they see much clear under the water.
- Most of the animals in jungle have better motion detection then human. They can see better in low light condition and detect smallest motion at distance. Cat’s field vision is almost 285 degrees – the ideal peripheral vision for hunting
- Sheep have large rectangular pupils that allow them to see at almost 360 degrees. They can see behind them without turning their heads.

Leave a comment